Chapter 15 by Nasha on Scribd
Saturday, 16 December 2017
Tuesday, 14 November 2017
Sunday, 5 November 2017
Sunday, 22 October 2017
Monday, 2 October 2017
Chapter 1
Business Driven Technology
Learning Outcomes
1.1 Compare management information systems (MIS) and information technology (IT)
1.2 Describe the relationships among people, information technology, and information
1.3 Identify four different departments in a typical business and explain how technology helps them to work together
1.4 Compare the four different types of organizational information cultures and decide which culture applies to your school
Information Technology's Role In Business

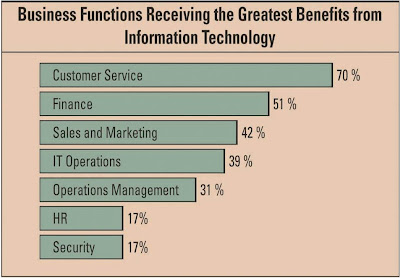
Information Technology's Impact On Business Operations

 Technology’s Role in
Technology’s Role in
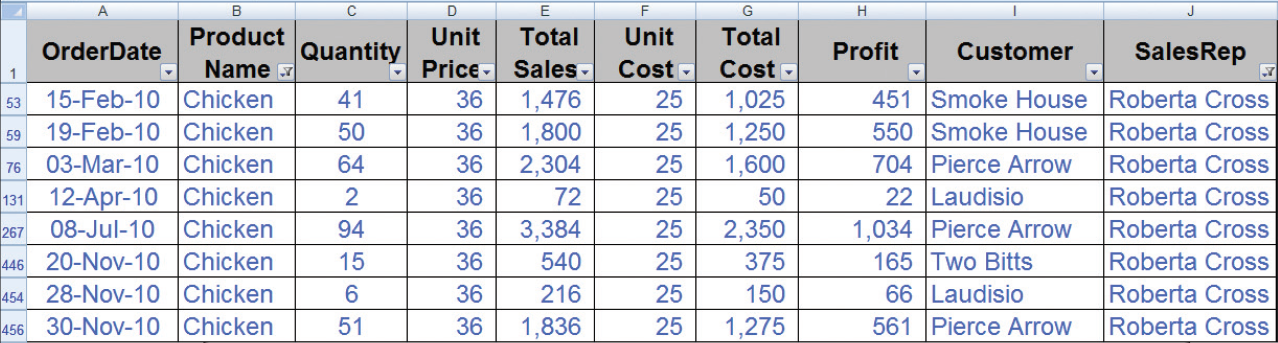
Data in an Excel Spreadsheet


Learning Outcomes
1.1 Compare management information systems (MIS) and information technology (IT)
1.2 Describe the relationships among people, information technology, and information
1.3 Identify four different departments in a typical business and explain how technology helps them to work together
1.4 Compare the four different types of organizational information cultures and decide which culture applies to your school
Information Technology's Role In Business

Information Technology's Impact On Business Operations


 Technology’s Role in
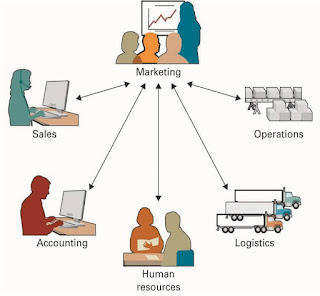
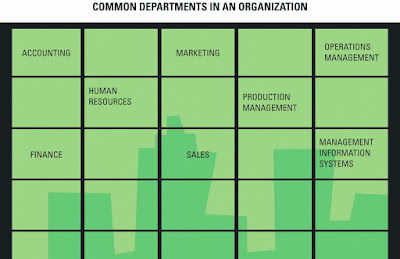
Technology’s Role in - Organizations typically operate by functional areas or functional silos
- Functional areas are interdependent
Information Technology Basics
- Information technology (IT) – a field concerned with the use of technology in managing and processing information
- Information technology is an important enabler of business success and innovation
- Management information systems (MIS) – a general name for the business function and academic discipline covering the application of people, technologies, and procedures to solve business problems
- MIS is a business function, similar to Accounting, Finance, Operations, and Human Resources
- When beginning to learn about information technology it is important to understand
- Data, information, and business intelligence IT
- resources
IT cultures
Information
- Data - raw facts that describe the characteristic of an
Information - data converted into a meaningful and
useful context
Business intelligence – applications and technologies that
are used to support decision-
making efforts
Data, Information and BI
Data in an Excel Spreadsheet
Data turned into information
Information turned into Business Intelligence
IT Resources
People use
Information technology to work
with
Information
IT Cultures
Organizational information cultures include:
Information-Functional Culture - Employees use information as a means of exercising influence or power over others. For example, a manager in sales refuses to share information with marketing. This causes marketing to need the sales manager’s input each time a new sales strategy is developed.
Information-Sharing Culture - Employees across departments trust each other to use information (especially about problems and failures) to improve performance.
Information-Inquiring Culture - Employees across departments search for information to better understand the future and align themselves with current trends and new directions.
Information-Discovery Culture - Employees across departments are open to new insights about crisis and radical changes and seek ways to create competitive advantages.
Monday, 18 September 2017
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
Chapter 15 : Outsourcing in the 21st Century
Chapter 15 by Nasha on Scribd
-
Chapter 10 by Nasha on Scribd
-
Chapter 12 by Nasha on Scribd
-
Chapter 13 by Nasha on Scribd